Submit feedback
Applications and Design Considerations for PP-R Inserts
Defining the PP-R Insert in Piping Systems
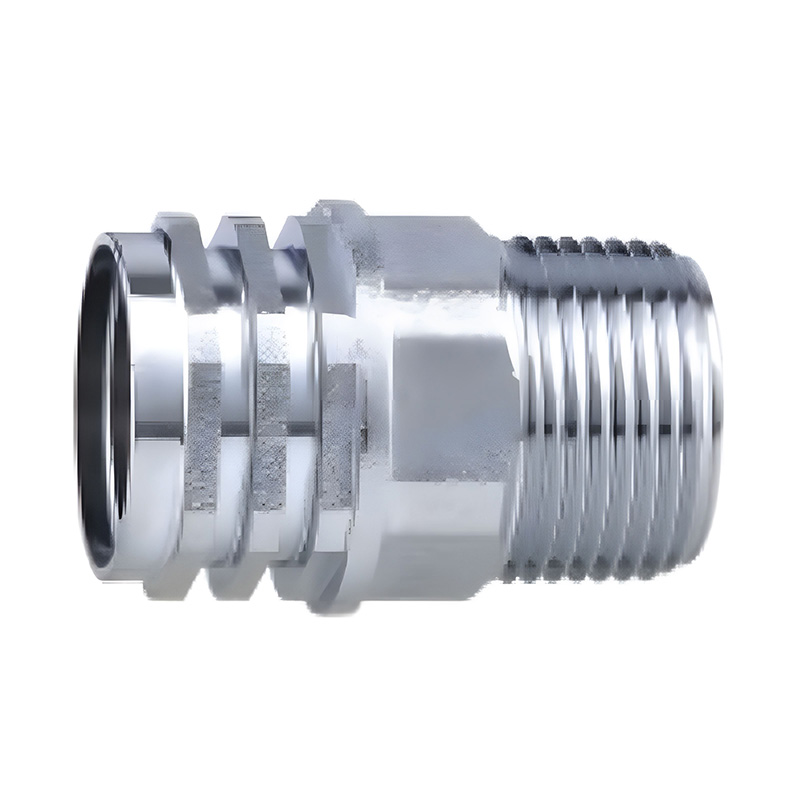
A pp-r insert refers to a molded or machined fitting component, typically made from brass, stainless steel, or a compatible engineering plastic, designed to be integrated into a Polypropylene Random Copolymer piping system. Its primary function is to provide a robust, threaded connection point within an otherwise fusion-welded plastic network. These inserts are commonly found in the form of threaded sockets, nuts, or connectors that are permanently fused onto the ends of PP-R pipes or fittings using the same heat-fusion process. The pp-r insert thus serves as a critical interface, enabling the reliable connection of PP-R systems to valves, pumps, fixtures, or other equipment that utilizes standard threaded ports, bridging the gap between the permanent plastic joints and the need for demountable, serviceable mechanical connections.

Material Compatibility and Fusion Integrity
The core engineering challenge for a pp-r insert lies in achieving a permanent, leak-proof bond between the metal (or alternative material) insert and the PP-R polymer. For metal inserts, the design often includes embedded fins, grooves, or a rough surface texture on the outer perimeter. During the fusion process, the heated PP-R material flows into these features, creating a strong mechanical interlock upon cooling that prevents pull-out under pressure or torque. The choice of insert material is crucial; brass alloys are common but must be lead-free and compatible with potable water standards. The thermal expansion coefficients of the metal and PP-R differ, so the design must account for this differential movement to maintain joint integrity over long-term thermal cycling, preventing stress concentration and potential failure at the fusion boundary.
Common Types and Standardized Applications
Pp-r inserts are standardized components tailored for specific functions. The most prevalent types include:
- Female Threaded Sockets: Fused onto a pipe end to receive a male-threaded valve or gauge.
- Male Threaded Adapters: Fused into a fitting to screw into a female-threaded port.
- Union Nuts with Olives: Used to create demountable unions between PP-R pipes and other components.
- Embedded Nuts for Fixtures: Designed for mounting taps, showerheads, or other wall-mounted fixtures directly onto PP-R stubs.
These standardized pp-r insert types allow installers to design systems with planned service points, cleanouts, or equipment interfaces without compromising the overall integrity of the fused PP-R network. Their dimensions and thread types conform to international standards to ensure interoperability.
Installation Process and Quality Assurance
Proper installation is vital for the performance of a pp-r insert. The process involves using a dual-heating tool with specific faces: one heats the end of the PP-R pipe or fitting, and the other heats the collar or fusion zone of the insert. After both parts reach the precise melt temperature, they are joined together with a straight, firm push and held steady during a defined cooling period without any twisting. Any deviation in heating time, temperature, or alignment can result in a weak joint. Quality assurance depends on visual inspection of the formed bead and, in critical applications, may involve pressure testing. The reliability of the entire threaded connection point hinges on the skill of the installer in executing this fusion process correctly with the pp-r insert.
Strategic Role in System Design and Maintenance
The strategic use of pp-r inserts significantly enhances the practicality and serviceability of PP-R piping systems. They enable modular design, allowing sections of the system to be isolated or removed for maintenance without cutting into the fused pipe. This is essential for installing and servicing control valves, meters, or filters. By providing reliable transition points, they extend the applicability of PP-R systems into complex industrial, commercial, and residential plumbing and heating installations where connections to existing equipment are necessary. Therefore, the pp-r insert is more than a simple connector; it is a fundamental enabler that allows the permanent, corrosion-resistant benefits of PP-R piping to be integrated into the broader, diverse world of fluid handling infrastructure.
 +86-13989680588
+86-13989680588 graylin@hongjiavalve.com
graylin@hongjiavalve.com